
Plant Disease Management
Powdery Mildew
Casual Agent
The disease is caused by the fungus Golovinomyces cichoracearum, which has a relatively wide host range compared to other powdery mildew fungi, encompassing many members of the plant families Asteraceae, Cucurbitaceae, and Solanaceae. The fungus is known as a biotroph, which means it needs living host tissue to survive. Once the host tissue is dead, the fungus must infect new host tissue to survive. The fungus grows on the epidermis of the host and does not penetrate deeply into plant tissue. Growth is favored by warm, relatively dry conditions. However, some relative humidity is required for disease development. Under such conditions, the fungus can produce millions of spores on the leaf surface and these spores are easily wind-borne to create new infections on neighboring plants. Under the right conditions, epidemics can be explosive and careful disease management is required to prevent such events.
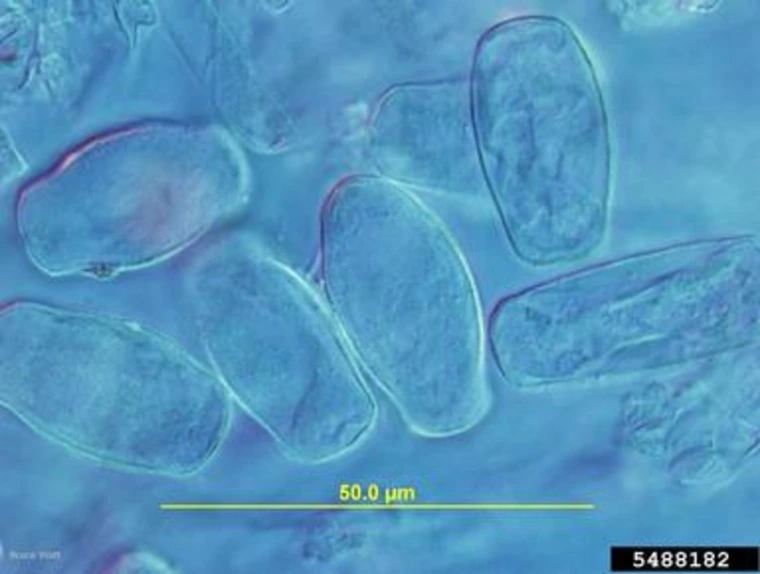
Golovinomyces cichoracearum: Bruce Watt, University of Maine, Bugwood.org

