
One Health
Wastewater-based Epidemiology (WBE)
Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) is the public health tool of the future. An early warning tool that harnesses public waste, wastewater-based surveillance can detect chemicals and pathogens in local wastewater systems, thus providing public health officials with valuable information about the status of well-being in a community. WBE can be used to coordinate and direct resources to reduce disease spread and prevent infections. The approach has been shown to save money and, more importantly, lives.
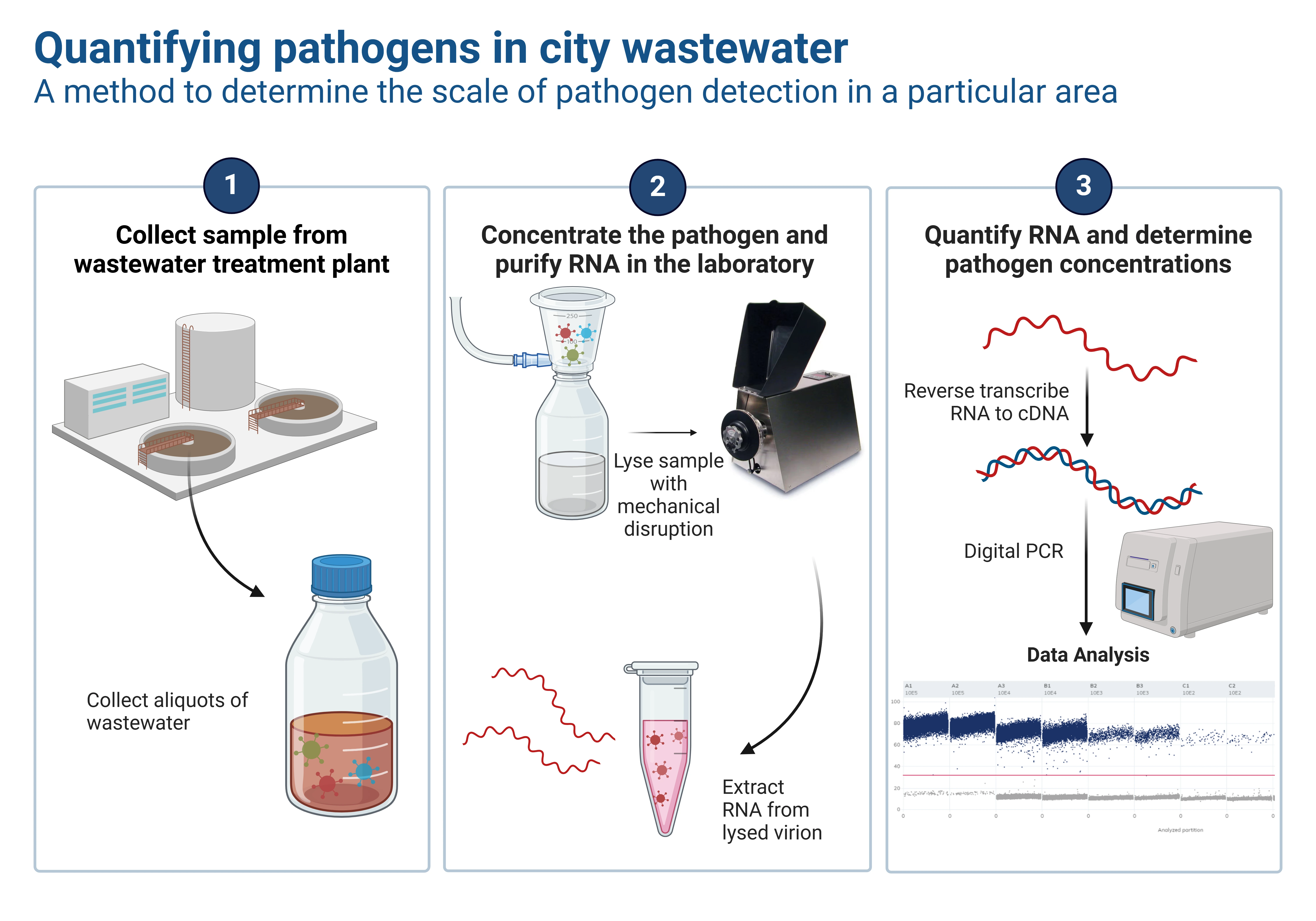
WBE relies on analyzing samples of wastewater to detect target chemicals or pathogens. The YCEDA laboratory collaborates with community partners to obtain samples and, in the case of biological targets, detection and quantification utilizes specialized equipment. The laboratory instrumentation includes: QIAcuity Digital PCR System and Illumina’s MiSeq Sequencing System. The graphic below illustrates the key steps in YCEDA's workflow for quantifying pathogens in community wastewater samples.
First employed during polio eradication efforts in the 1940s, WBE expanded over time to screen for several other chemical and biological disease indicators. As a non-invasive and population-level tool, WBE became mainstream globally during the COVID-19 pandemic. The potential applications in public health are limitless. It can track disease trends, enumerate affected individuals, and inform a nimble public health policy. We have barely scratched the surface of wastewater applications to promote One Health efforts, including those focusing on animal health.
Target List | |
|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 | Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) |
| Influenza A/B (Flu A/B) | West Nile Virus (WNV) |
| Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) | Dengue (DENV)* |
| Candida auris | Adenovirus (ADV)* |
| Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) | Norovirus GI/GII (NVG)* |
| *Pathogen targets initiated on an as-needed basis | |

